Extrusion Methods of Aluminum Profiles: Forward and Backward Extrusion Explained
Release Time:
2024-04-18
The extrusion methods of aluminum profiles are classified based on the direction, mainly determined by the movement of the extrusion axis concerning the aluminum product's movement. Forward extrusion, also known as direct extrusion, entails the aluminum ingot's flow direction aligning with the rotation direction of the extrusion axis.
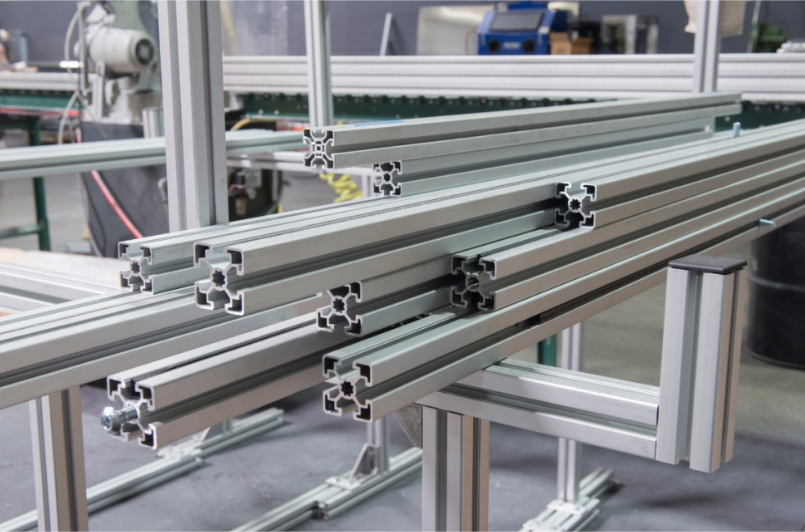

During this process, the metal flows along the extrusion axis towards the die orifice, resulting in compressed products with higher density and mechanical performance.
However, attention is required to mitigate sliding friction between the billet and the extrusion cylinder, which can affect product uniformity and increase energy consumption and mold wear. Measures such as lubrication, material selection, and controlling extrusion temperature and speed are crucial to minimize friction and enhance product quality.
On the other hand, backward extrusion, or indirect extrusion, involves the aluminum ingot's flow direction opposing the rotation direction of the extrusion axis. Although this method presents challenges in surface quality control and complexity in operation, it offers unique advantages in certain production requirements and product applications.

Modern extrusion machines equipped with movable extrusion cylinders accommodate backward extrusion demands. Surface treatment techniques and careful design considerations address surface quality issues, while despite its longer cycle time and operational complexity, backward extrusion compensates with increased product dimensions, reduced scrap, and enhanced production efficiency.
While each extrusion method suits distinct production needs—forward extrusion for high-strength, high-density products like architectural aluminum profiles and high-speed rails, and backward extrusion for high-volume, elongated products such as doors, windows, and radiators.
Previous
More News

2024/05/03
Principles and Application Scope of Microchannel
Microchannels, also known as microchannel heat exchangers, are heat exchangers with channel equivalent diameters ranging from 10-1000μm. These heat exchangers feature dozens of fine flow channels inside a flat tube, connected to circular manifolds at both ends of the flat tube.

2024/04/26
Exploring Pillow Plate Technology
Pillow plates represent a captivating advancement in engineering, crafted through an innovative inflation process. This technique involves seamlessly welding together two sheets of stainless steel or mild steel using sophisticated laser or resistance welding methods.

2024/04/18
Extrusion Methods of Aluminum Profiles: Forward and Backward Extrusion Explained
The extrusion methods of aluminum profiles are classified based on the direction, mainly determined by the movement of the extrusion axis concerning the aluminum product's movement.