Project Case
Heat Sinks in Power Electronics: Essential Components for Efficient Thermal Management
In modern power electronics, managing heat is one of the most critical challenges. Power electronic devices, such as power supplies, inverters, electric vehicles, and industrial machinery, generate significant amounts of heat during operation. Without efficient heat management, these devices can overheat, causing performance degradation, reduced lifespan, and even complete failure. This is where heat sinks come into play, particularly in applications involving high-power devices.
A heat sink is a passive thermal management component designed to absorb and dissipate heat from electronic components. They are essential in power electronics to maintain safe operating temperatures and ensure long-term reliability and performance. This article will explore how heat sinks are used in power electronics, with a focus on various types, such as custom heat sinks, extruded aluminum heat sinks, high-performance heat sinks, and liquid-cooled heat sinks. We will also look at how these technologies play a crucial role in industrial thermal management.
The Importance of Heat Sinks in Power Electronics
In power electronics, devices like transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits can generate significant heat during operation. This heat must be managed efficiently to prevent overheating and ensure that these devices operate at optimal performance levels. Failure to do so can lead to thermal damage, resulting in system failure and even the need for expensive replacements or repairs.
Heat sinks provide a way to absorb and dissipate this heat away from sensitive electronic components. By increasing the surface area that comes in contact with the surrounding air or fluid, heat sinks help to transfer heat from the electronic device to the environment, maintaining the temperature within safe limits.
How Heat Sinks Work in Power Electronics
A heat sink works based on the principle of thermal conduction. It absorbs heat from the hot electronic component (like a power transistor or diode) and transfers it to its surface. The heat is then dissipated into the surrounding air or liquid through thermal convection and radiation.
The efficiency of a heat sink is determined by its ability to increase the surface area, improve airflow, and ensure effective heat dissipation. The material used for manufacturing the heat sink is also crucial; materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum and copper, are commonly used to ensure that heat is transferred effectively.
Types of Heat Sinks for Power Electronics
Several types of heat sinks are used in power electronics applications, each designed to meet specific thermal management needs. These include extruded aluminum heat sinks, custom heat sinks, high-performance heat sinks, and liquid-cooled heat sinks. Let’s take a closer look at each type.
1. Custom Heat Sinks
In power electronics, one-size-fits-all solutions do not always work due to the unique thermal requirements of different devices. Custom heat sinks are designed to meet the specific needs of a particular application, offering a tailored approach to thermal management.
Custom heat sinks are often designed with advanced simulations and calculations to ensure they can effectively dissipate heat based on the power dissipation, environment, and device specifications. For instance, if a power module is unusually large or generates more heat than a standard module, a custom heat sink can be designed to accommodate these unique needs, ensuring that heat is effectively managed.
2. Extruded Aluminum Heat Sinks
Extruded aluminum heat sinks are one of the most common types of heat sinks used in power electronics due to their cost-effectiveness and excellent thermal performance. The extrusion process involves forcing aluminum through a mold to create a heat sink with a specific shape, typically with fins that maximize the surface area for heat dissipation.
The extrusion process allows for efficient mass production of heat sinks, making them an ideal choice for commercial power electronics. Aluminum is also lightweight, durable, and has high thermal conductivity, making it a popular material for heat sinks in various power electronics applications. They are especially suited for applications with moderate to high power dissipation.
Extruded aluminum heat sinks are ideal for power electronics devices like power supplies, LED drivers, and industrial power converters, where space, cost, and performance need to be balanced.
3. High-Performance Heat Sinks
For power electronics devices that operate under high loads and extreme conditions, high-performance heat sinks are often required. These heat sinks are designed to provide superior thermal management, even in environments where standard heat sinks might struggle.
High-performance heat sinks are often made from materials like copper or high-quality aluminum alloys that have superior thermal conductivity. They also feature advanced fin designs, including pin fins, dimpled surfaces, and micro-fins, which enhance the surface area for heat dissipation and improve airflow around the device.
In addition to material choice, high-performance heat sinks also utilize advanced manufacturing techniques like laser welding and precision machining to ensure that they provide maximum thermal performance. These heat sinks are typically used in power electronics applications that involve high currents or high frequencies, such as high-power inverters, electric vehicles, solar inverters, and data centers.
4. Liquid-Cooled Heat Sinks
While air-cooled heat sinks are commonly used in many power electronics applications, there are cases where liquid-cooled heat sinks provide a better solution. Liquid cooling involves using a liquid, typically water or a specialized coolant, to transfer heat from the heat sink to a cooling system, such as a radiator or cooling tower.
Liquid-cooled heat sinks are ideal for applications where heat dissipation requirements are very high. Since liquids have a much higher heat capacity than air, they can absorb and transport more heat. As a result, liquid-cooled heat sinks offer greater cooling efficiency in applications such as high-power electronics, data centers, electric vehicle charging stations, and industrial machinery.
These heat sinks often feature channels or microchannels through which the coolant flows, absorbing heat from the heat sink and carrying it away to be dissipated elsewhere. Liquid-cooled heat sinks are particularly useful in situations where air cooling is insufficient to maintain safe operating temperatures.
Benefits of Using Heat Sinks in Power Electronics
Improved Reliability and Longevity
By effectively managing the temperature of power electronic devices, heat sinks play a key role in extending the lifespan of these components. When components are kept within their optimal operating temperature range, they are less likely to suffer from thermal stress, which can lead to early failure.
Enhanced Efficiency
Power electronics systems operate more efficiently when their temperature is carefully controlled. Overheating can lead to energy loss and decreased performance. Heat sinks ensure that devices maintain efficient operation, even under heavy load conditions.
Cost-Effective Thermal Management
Heat sinks, especially extruded aluminum heat sinks, offer a cost-effective solution to thermal management. The relatively low manufacturing cost and high availability of materials make heat sinks a practical solution for industries that require affordable yet efficient cooling solutions.
Compact Design
Heat sinks are typically compact and lightweight, which makes them ideal for integration into power electronic systems where space is limited. Their small footprint allows them to be used in a wide range of applications, from small consumer electronics to large industrial systems.
Environmental Benefits
Since heat sinks are passive components, they do not require electricity to operate. They rely on natural convection and conduction to dissipate heat, which makes them environmentally friendly. Furthermore, high-performance heat sinks reduce the need for additional cooling mechanisms, such as fans or air conditioning, leading to lower energy consumption.
Applications of Heat Sinks in Power Electronics
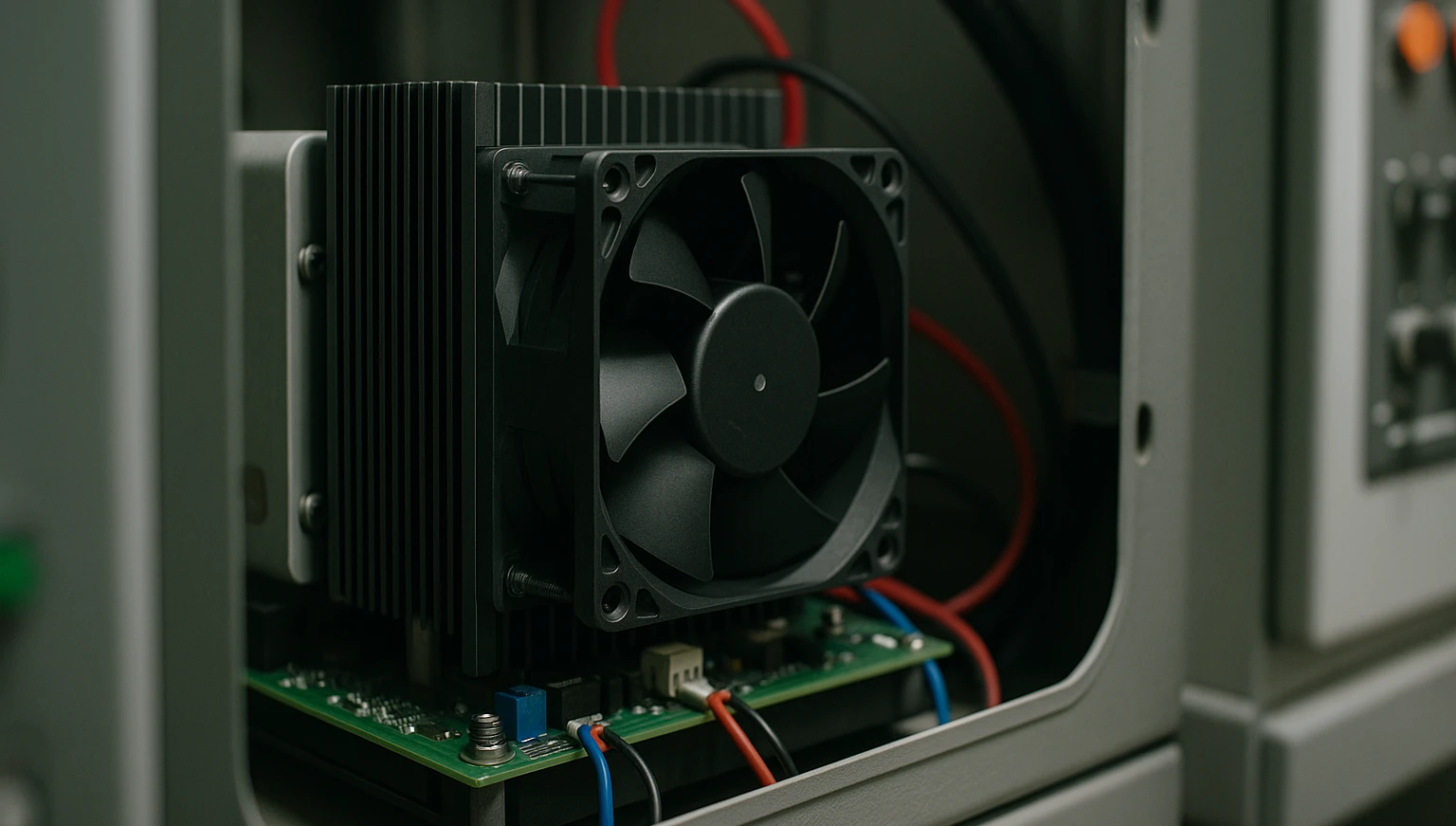

Power Supplies
Power supplies are essential in most electronic systems, converting electrical energy from one form to another. Power supplies often involve high-power devices that generate substantial heat. Heat sinks ensure that these components remain within safe operating temperatures, preventing overheating and ensuring reliable operation.
Inverters and Converters
Inverters and converters are critical components in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and industrial machinery. These devices convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) and vice versa, generating significant amounts of heat. Heat sinks play a vital role in maintaining efficient operation in these high-power systems.
LED Drivers
LED drivers are another common application where heat sinks are essential. High-power LEDs generate heat that must be dissipated to ensure optimal light output and to prevent premature failure. Heat sinks help extend the life of LEDs by preventing them from overheating.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
As electric vehicles become more mainstream, the demand for efficient power electronics has risen. EVs rely on power electronics to manage battery charging, energy conversion, and motor control. Heat sinks in these applications are crucial for ensuring the performance and longevity of the power modules used in EV systems.
Data Centers
Data centers house thousands of servers that process vast amounts of data. These servers generate considerable heat, which must be managed to avoid system downtime. Heat sinks are used extensively in these systems to ensure that processors and other components maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Conclusion
As power electronics continue to evolve, the importance of effective thermal management becomes even more critical. Heat sinks are essential components in ensuring that power electronic devices operate efficiently, reliably, and for extended periods. Whether through custom heat sinks, extruded aluminum heat sinks, high-performance heat sinks, or liquid-cooled heat sinks, industries can ensure that their systems stay within safe thermal limits.
NANJING METALLI INDUSTRIAL CO., Ltd. offers a wide range of heat sink solutions designed for power electronics, helping businesses optimize their thermal management and improve the performance of their systems. With advanced materials, custom designs, and a commitment to quality, they are well-positioned to meet the ever-growing demands of industrial thermal management.